railway-international.com
28
'25
Written on Modified on
Everything You Need to Know About Single Phase Solid State Relays: Advantages and Applications
celduc relais dives into the operation of single-phase SSRs, explore their advantages over electromechanical relays, and look at their real-world applications in both industrial and residential settings.
railway-news.com

In an increasingly automated and energy-efficient world, single-phase solid-state relays (SSRs) stand out as essential components in modern heating and lighting systems. These extraordinary devices replace traditional electromechanical relays with cutting-edge electronic technology, offering significant advantages: ultra-fast switching, completely silent operation, and exceptional durability.
But how do these relays actually work? Why have they become indispensable in applications ranging from industrial heating systems and ventilation to residential and commercial lighting? In this article, we’ll dive into the operation of single-phase SSRs, explore their advantages over electromechanical relays, and look at their real-world applications in both industrial and residential settings. Get ready to discover why these solid-state relays are the ideal solution for precise, reliable, and silent control of your electrical systems.
1. How single phase SSR work
Single-phase SSRs are non-mechanical switching devices that use semiconductor components (like triacs or thyristors) to control AC loads. When a small control voltage is applied to the input terminals, it activates an internal LED. The light from this LED is detected by a photosensitive component (a phototransistor or similar device), which then triggers the main semiconductor switch to allow current to flow to the load. This optical isolation between the control circuit and the load circuit prevents electrical noise and provides an extra layer of safety. This makes SSRs particularly advantageous in environments where electromagnetic interference could disrupt sensitive control electronics.
Known for their silent operation, fast response times, and high durability, SSRs are especially effective in applications where precision and long life cycles are crucial, such as electric heating systems and lighting control.
2. Key advantages of Single-Phase SSRs
Advantages in Heating and Lighting Applications:
In heating applications, single-phase SSRs can quickly cycle power to heating elements to maintain a constant temperature, avoiding the temperature overshoot and undershoot often seen with slower mechanical relays. For lighting, especially with incandescent or halogen lamps, SSRs can provide dimming control by using a technique called phase-angle control, which modulates the amount of power delivered to the lamp. The silent operation, long lifespan, and lack of electrical arcing make them a superior choice for both residential and industrial settings, improving both system performance and safety.
Advantages over ElectroMechanical Relays (EMRs):
For heating and lighting applications that require precise control, single-phase SSRs offer several key benefits over EMRs:
- Longer Lifespan: With no moving parts to wear out or contacts to arc and degrade, SSRs can last for millions of cycles. This is a critical advantage in systems that require frequent on/off cycling to maintain a steady temperature.
- Faster Switching: SSRs can switch within milliseconds, much faster than the typical 10-20 ms of an EMR. This speed is essential for sophisticated control methods like Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control, which rapidly modulates power to the heater to eliminate temperature fluctuations.
- Silent Operation: The absence of mechanical contacts means SSRs operate silently, making them ideal for use in residential, medical, and other noise-sensitive environments.
- Reduced EMI: Zero-cross switching significantly reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which can be a major issue with EMRs.
3. Technical considerations
celduc® relais offers a wide range of single phase Solid State Relays. Single phase solid state relays have specifications that vary depending on the model, but certain characteristics are common across most units. They are ideally suited for controlling resistive loads, although some models can also handle inductive loads. In terms of voltage rating, single-phase SSRs typically operate within a range of 24 to 660 VAC, making them versatile for a wide variety of electrical applications. The current rating varies by model, with common ranges from 10 to 125 amps, allowing them to meet specific needs based on the load being controlled.
To ensure efficient heat dissipation and prevent overheating, SSRs require heatsinks and thermal pads/compounds. These components are crucial for maintaining an optimal operating temperature and extending the lifespan of the relays. Finally, regarding the control voltage, SSRs generally operate within a range of 3 to 32 VDC, making them compatible with systems like programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and other types of controllers.
4. Applications in Heating Systems
How SSRs work for Heating Segment
Most SSRs designed for heating applications utilize a feature called zero-cross switching. This means the relay only turns on when the AC voltage waveform crosses the zero-volt line. This minimizes the inrush current and high-frequency electrical noise that can be generated when switching resistive loads, thereby extending the life of the heating element and protecting other sensitive equipment in the system.
In electric heating systems (like ovens, industrial heaters, and floor heating), SSRs control resistive loads by turning the heating element on and off based on signals from a temperature controller or programmable logic controller (PLC). See schematic example below:
celduc® relais offers a wide range of single phase Solid State Relays. Single phase solid state relays have specifications that vary depending on the model, but certain characteristics are common across most units. They are ideally suited for controlling resistive loads, although some models can also handle inductive loads. In terms of voltage rating, single-phase SSRs typically operate within a range of 24 to 660 VAC, making them versatile for a wide variety of electrical applications. The current rating varies by model, with common ranges from 10 to 125 amps, allowing them to meet specific needs based on the load being controlled.
To ensure efficient heat dissipation and prevent overheating, SSRs require heatsinks and thermal pads/compounds. These components are crucial for maintaining an optimal operating temperature and extending the lifespan of the relays. Finally, regarding the control voltage, SSRs generally operate within a range of 3 to 32 VDC, making them compatible with systems like programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and other types of controllers.
4. Applications in Heating Systems
How SSRs work for Heating Segment
Most SSRs designed for heating applications utilize a feature called zero-cross switching. This means the relay only turns on when the AC voltage waveform crosses the zero-volt line. This minimizes the inrush current and high-frequency electrical noise that can be generated when switching resistive loads, thereby extending the life of the heating element and protecting other sensitive equipment in the system.
In electric heating systems (like ovens, industrial heaters, and floor heating), SSRs control resistive loads by turning the heating element on and off based on signals from a temperature controller or programmable logic controller (PLC). See schematic example below:
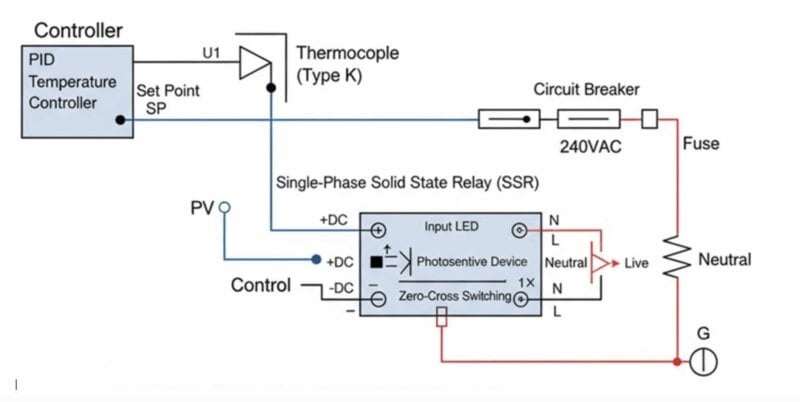
Applications with Single-Phase Heaters
SSRs are used in a wide range of heating applications where stable, precise, and reliable temperature control is required such as:
Industrial Furnaces and Ovens:
In industries like plastics, ceramics, and food processing, industrial furnaces and ovens require extremely tight temperature control for consistent product quality. An SSR, controlled by a temperature controller, can rapidly cycle a single-phase heating element to maintain a precise setpoint, preventing temperature overshoot and undershoot.
Plastic Injection Molding:
The barrel and nozzle of plastic injection molding machines are equipped with heating bands that need precise temperature regulation. Single-phase SSRs are used to control these heating elements, ensuring the plastic material is at the exact temperature required for molding without degradation.
HVAC Systems:
In modern HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, single-phase SSRs are often used to control electric heating elements in air ducts. Their fast switching and silent operation allow for efficient and comfortable heating. They can also be used in residential baseboard heaters and high-voltage floor heating.
Professional Food Equipment:
Single-phase SSRs are widely used in professional kitchen appliances like commercial coffee makers, fryers, and grills. They provide the reliable and precise temperature control needed to ensure consistent cooking results and energy efficiency.
5. Applications in Lighting Control
How SSRs Work for Lighting Segment
Two common switching methods are used with single-phase SSRs in lighting:
- Zero-Cross Switching: This type of SSR only turns on when the AC voltage waveform crosses the zero-volt line. This is ideal for simple on/off switching of lamps. By turning on at the zero-crossing point, it minimizes the inrush current that is common with incandescent and halogen lamps. This inrush current can be up to 10 to 15 times the normal operating current of a lamp, and zero-cross switching helps to reduce stress on the lamp’s filament, extending its lifespan.
- Phase-Angle Control: This method is used for dimming applications. A phase-angle controlled SSR, often called an “analog control SSR,” doesn’t wait for the zero-cross point. Instead, it is triggered at a specific point within each half-cycle of the AC waveform. By controlling the timing of this trigger, you can vary the amount of power delivered to the lamp, thereby controlling its brightness. A small control voltage or current ( 0-10 VDC or 4-20 mA) is used to precisely control the trigger point. See example schematic below:
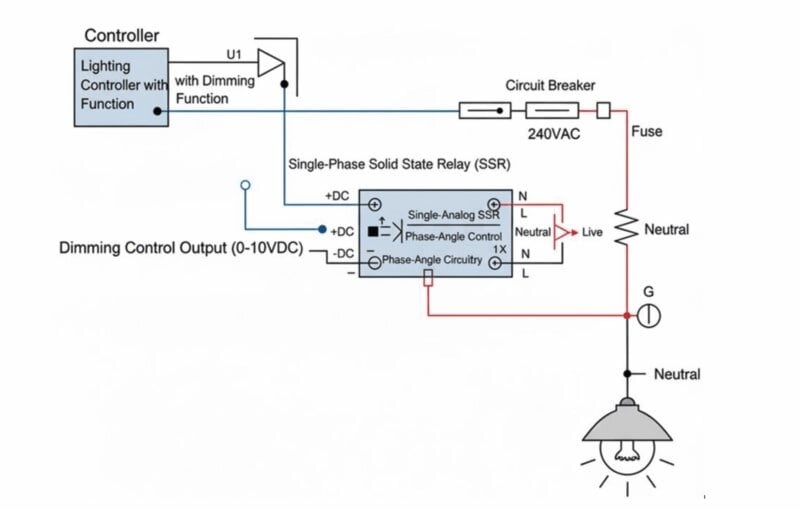
Lighting Applications with SSRs
Single-phase SSRs are used in a variety of lighting applications, from simple on/off control to complex dimming systems such as:
Residential and Commercial Lighting Control:
In home automation and smart building systems, SSRs are used to control groups of lights. Their long lifespan and silent operation make them a reliable alternative to traditional wall switches or contactors. For dimmable lighting, a phase-angle controlled SSR can be integrated with a dimmer or a central control unit to provide smooth and precise brightness adjustments.
Theatrical and Stage Lighting:
For stage productions and concerts, SSRs are critical for controlling lighting effects. Their fast switching speed enables chaser lights and strobing effects with perfect synchronization. Phase-angle control allows lighting designers to create a wide range of moods and visual effects with granular control over brightness.
Public and Industrial Lighting:
In public spaces like streets, airports, and warehouses, large banks of lights can be controlled efficiently with SSRs. Zero-cross switching is often used here to manage the high inrush currents of numerous discharge lamps or LEDs at once. The reliability of SSRs ensures that public lighting systems are less prone to failure and require minimal maintenance.
Emergency Lighting Systems:
SSRs can be used in emergency lighting systems to switch on backup lighting instantly during a power outage. Their fast response time and reliability are paramount in safety-critical applications.
Conclusion
Solid state relays offer a robust, reliable, and efficient solution for modern heating and lighting applications. Their precision and durability make them a preferred choice across industrial, commercial, and residential settings. As demand for energy-efficient and digitally controlled systems grows, SSRs will continue to be a essential component in automation and smart infrastructure.
www.celduc-relais.com

